Pull Request Testing
Our first and optimal chance to catch regressions is prior to pull requests merging, preventing any impact to the payloads.
Presubmits
Presubmit jobs are configured for each repository and an obvious first possibility to catch a regression. They can be required or optional and we do know that historically problems can slip through unnoticed in optional presubmits.
Risk Analysis
Risk Analysis is an attempt to prevent regressions that surface during presubmit testing from slipping through merge, either because they occurred in an optional job, or because they happened a few times and then passed.
Risk Analysis begins with an API call in Sippy where the failures in a job run are submitted for analysis. Sippy checks the pass rate for each of those tests over the past several weeks, matching the specific variants of the job in question. If the test commonly flakes, that failure would be categorized as low risk. If that test passed 100% of the time, it would be categorized as high. The worst risk level for a specific test is then bubbled up as the risk level for the overall job failure.
We call this API at the end of the core e2e test step in the release repo, and generate the html artifact that is ultimately displayed in the prow UI.
Note that risk analysis is not doing any kind of code analysis, it is purely checking how common the job runs test failures were.
| Historical Pass Rate % | Risk Analysis Ranking |
|---|---|
| 100 - 98 | High |
| 97 - 80 | Medium |
| < 80 | Low |
Artifacts are created under the e2e test junit directory like test-failures-summary_20230706-065159.json and the final
analysis test-risk-analysis.html. When available, the test-risk-analysis.html
summarization will show in the prow job spyglass view under the Risk Analysis
heading. The view will show the Test Name, Risk Level, Risk Reason and
Open Bugs. At the top of the table the Test Name Overall will
show the highest risk value. The Open Bugs
are listed to surface any known issues with the test that may be impacting the results. Additionally,
a link to Sippy is provided at the top of the section to aid in further investigation. If your job is not run by a step that includes
the Risk Analysis artifacts generation, or the junits fail to run, the Risk Analysis artifacts will not be present.
| Test Name | Risk Level | Risk Reason | Open Bugs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | High | Maximum failed test risk: High | |
| [bz-DNS][invariant] alert/KubePodNotReady should not be at or above info in ns/openshift-dns | High | This test has passed 100.00% of 928 runs on jobs [‘periodic-ci-openshift-release-master-ci-4.14-upgrade-from-stable-4.13-e2e-azure-sdn-upgrade’] in the last 14 days. |
If there are too many test failures the Overall Risk Level will be High with a message showing the number of failed tests.
| Test Name | Risk Level | Risk Reason | Open Bugs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | High | 53 tests failed in this run: High |
If there are too few tests run,
compared to historical runs, a message indicating IncompleteTests will be
shown.
| Test Name | Risk Level | Risk Reason | Open Bugs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | High | Tests for this run (47) are below the historical average (1432): IncompleteTests |
PR Commenting
For repos with Risk Analysis PR commenting enabled (currently just origin), a comment will be added to the PR ranking the failure risk for each job with an associated risk once all of the current jobs complete. The comment contains the sha that is associated with the job runs and lists the Job Names (as a link to the job run results) ranking them by Failure Risk from high to low. Each job row will contain the test failures that match the overall risk level for that job, the risk reason for each test failure and any known bugs associated with the test.
In an effort to reduce flagging flaky tests, PR Commenting will only include tests that have failed in consecutive jobs.
Job Failure Risk Analysis for sha: 79d237196d93eb92ed58c66497d8718259264226
| Job Name | Failure Risk |
|---|---|
| pull-ci-openshift-origin-master-e2e-gcp-ovn-upgrade | High [sig-api-machinery] disruption/cache-oauth-api connection/reused should be available throughout the test: This test has passed 99.88% of 827 runs on jobs [‘periodic-ci-openshift-release-master-nightly-4.14-e2e-gcp-ovn-upgrade’ ‘periodic-ci-openshift-release-master-ci-4.14-e2e-gcp-ovn-upgrade’] in the last 14 days. |
| pull-ci-openshift-origin-master-e2e-metal-ipi-ovn-ipv6 | Low [sig-network][Feature:vlan] should create pingable pods with macvlan interface on an in-container master [apigroup:k8s.cni.cncf.io] [Suite:openshift/conformance/parallel]: This test has passed 72.09% of 43 runs on jobs [‘periodic-ci-openshift-release-master-nightly-4.14-e2e-metal-ipi-ovn-ipv6’] in the last 14 days. — [sig-cli] oc idle [apigroup:apps.openshift.io][apigroup:route.openshift.io][apigroup:project.openshift.io][apigroup:image.openshift.io] by name [Suite:openshift/conformance/parallel]: This test has passed 72.09% of 43 runs on jobs [‘periodic-ci-openshift-release-master-nightly-4.14-e2e-metal-ipi-ovn-ipv6’] in the last 14 days. Open Bugs https://issues.redhat.com/browse/OCPBUGS-6586 — [sig-network][Feature:tuning] pod should start with all sysctl on whitelist [apigroup:k8s.cni.cncf.io] [Suite:openshift/conformance/parallel]: This test has passed 72.09% of 43 runs on jobs [‘periodic-ci-openshift-release-master-nightly-4.14-e2e-metal-ipi-ovn-ipv6’] in the last 14 days. — [sig-network][Feature:bond] should create a pod with bond interface [apigroup:k8s.cni.cncf.io] [Suite:openshift/conformance/parallel]: This test has passed 72.09% of 43 runs on jobs [‘periodic-ci-openshift-release-master-nightly-4.14-e2e-metal-ipi-ovn-ipv6’] in the last 14 days. |
The job name links can be used to review the failures to further analyze if the changes within the PR might be impacting the test failures.
How to use Risk Analysis
Risk Analysis is not intended to indicate a particular code change or set of code changes is the source of regression, it is intended to raise awareness that the risk of regression may be elevated based on the failures of tests that consistently pass at a high rate. You can use Risk Analysis as a guide to identify jobs to investigate closer to see if the failures may be related to recent changes.
Payload Commands
OpenShift engineering has the capability to run a selected subset of release qualification jobs on selected pull requests in all repositories that contribute to OCP, before they are merged.
The PullRequestPayloadQualificationRun CRD and the /payload command is provided for this purpose. These commands will build an OpenShift payload with the code for the current pull request, and initiate prow jobs against that payload.
/payload
This command can be used to launch all blocking or informing jobs for a given OpenShift release and nightly/ci stream.
WARNING: This can be very expensive, all blocking jobs on a development release will be about 50 jobs, informing is around 80 jobs. This also places strain on our cloud/metal/vsphere quotas. This command should be used when a change is high risk for breaking the payload, but sparingly whenever possible. More targeted options are available and described below.
Examples when /payload blocking/informing should be used:
- Major Kube rebases, CoreOS updates, ovn/network upgrades.
- New invariant tests that could start failing payloads.
Examples when /payload blocking/informing should not be used:
- To gather results for a specific job. (see /payload-job and /payload-aggregate below)
- Any low risk change.
Any collaborator of the GitHub OpenShift organization can issue the command on a pull request to a branch of a repository of the organization that contributes to OpenShift official images:
/payload <ocp_version> <ci|nightly> <informing|blocking>
For example, if /payload 4.10 nightly informing is issued on a PR, the robot will reply the list of the triggered jobs:
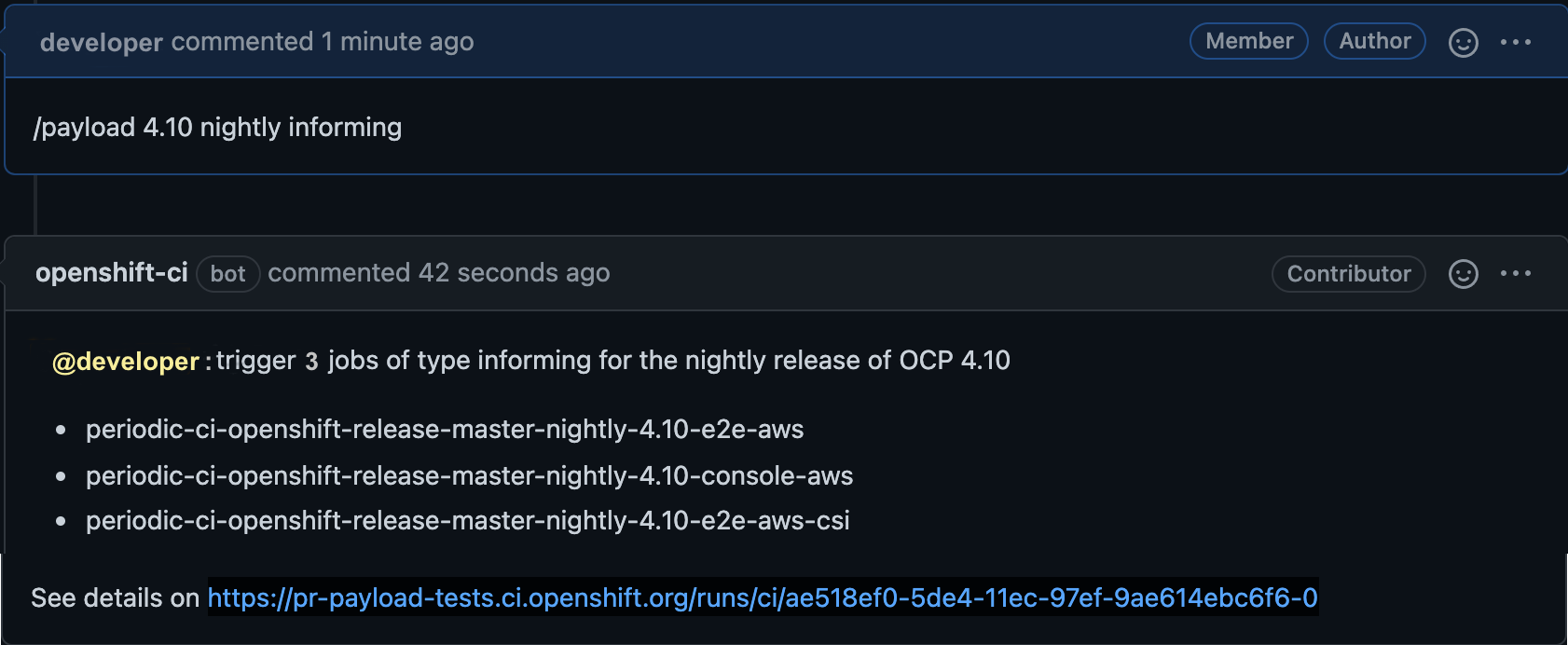
The jobs triggered by the command are determined by OpenShift Release Controllers.
The linked page from payload-tests portal at the bottom of the comment shows the status of the payload testing and the details of those jobs.
You can also invoke this command with multiple PRs:
/payload-with-prs <ocp_version> <ci|nightly> <informing|blocking> <org/repo#number> [<org/repo#number ...]
/payload-job
A particular job or set of jobs can be triggered by /payload-job, such as
/payload-job <periodic_ci_openshift_release_some_job> <periodic_ci_openshift_release_another_job>
This command can be repeated in one comment to launch multiple copies of the same job. (this differs from /payload-aggregate which will attempt Fisher’s Exact test on the results)
You can also invoke this command with multiple PRs:
/payload-job-with-prs <periodic_ci_openshift_release_some_job> <org/repo#number> [<org/repo#number ...]
/payload-aggregate
It is also possible to perform aggregation on any of these jobs with /payload-aggregate. This launches the specified number of job runs, and attempts aggregation with Fisher’s Exact.
/payload-aggregate <periodic_ci_openshift_release_some_job> <aggregated_count>
You can also invoke this command with multiple PRs:
/payload-aggregate-with-prs <periodic_ci_openshift_release_some_job> <aggregated_count> <org/repo#number> [<org/repo#number ...]
/payload-with-prs,/payload-aggregate-with-prs, and/payload-job-with-prsonly accept a single command per comment; additional commands need to be triggered with separate comments (not just separate lines).- The jobs used in the payload commands above are periodics. Presubmits are not supported at the moment, which is different from the
/testwithcommand.
/payload-abort
It is possible to quickly abort all running payload jobs for a specific PR. Simply comment /payload-abort on the PR to do so.
This is particularly helpful when a large number of jobs have been launched.
Manually Submitting a PRPQR
It is also possible to manually create a PullRequestPayloadQualificationRun instance without using the payload command.
This allows for additional options to be supplied that are currently not possible via the command.
The following is an example of a full PRPQR CR that can be applied to the app.ci cluster to trigger a payload job:
| |
If multiple pullRequests entries are supplied for a single org/repo pair, the baseRef and baseSHA will be selected only from the first one in the list.
Therefore, it is not supported to have differing entries for these.
Supplying Multiple PRs from Component Repositories
The ci-operator can assemble a release payload by building and using images from multiple PRs in OCP component repos.
In order to do this, refs for each PR must be provided in the PRPQR spec:
| |
Overriding the Default Payload PullSpecs
It is possible to override the pull-spec used for both the initial and latest release payloads by manually submitting a PRPQR.
This is done by supplying the spec.initial and spec.payload.base fields respectively:
| |
Overriding Specific Image Tags in the Payload
It is also possible to override a specific image tag in the payload to any arbitrary pullspec. Doing so requires manually submitting a PRPQR.
This can be done by providing the tag overrides in the spec.payload.tags list:
Sourcing Components from Specific Base
A PRPQR can be submitted without referencing an open PR. This is useful to pin one or more component repos to a specific baseRef and baseSHA in order to test the state of things at that point.
Doing so requires manually applying the PRPQR CR: